Understanding Corneal Inflammation in Cats
When it comes to feline eye health, corneal inflammation, also known as eosinophilic keratitis, is a common condition that affects cats. Understanding the overview and causes of corneal inflammation is essential for cat owners.
Overview of Corneal Inflammation
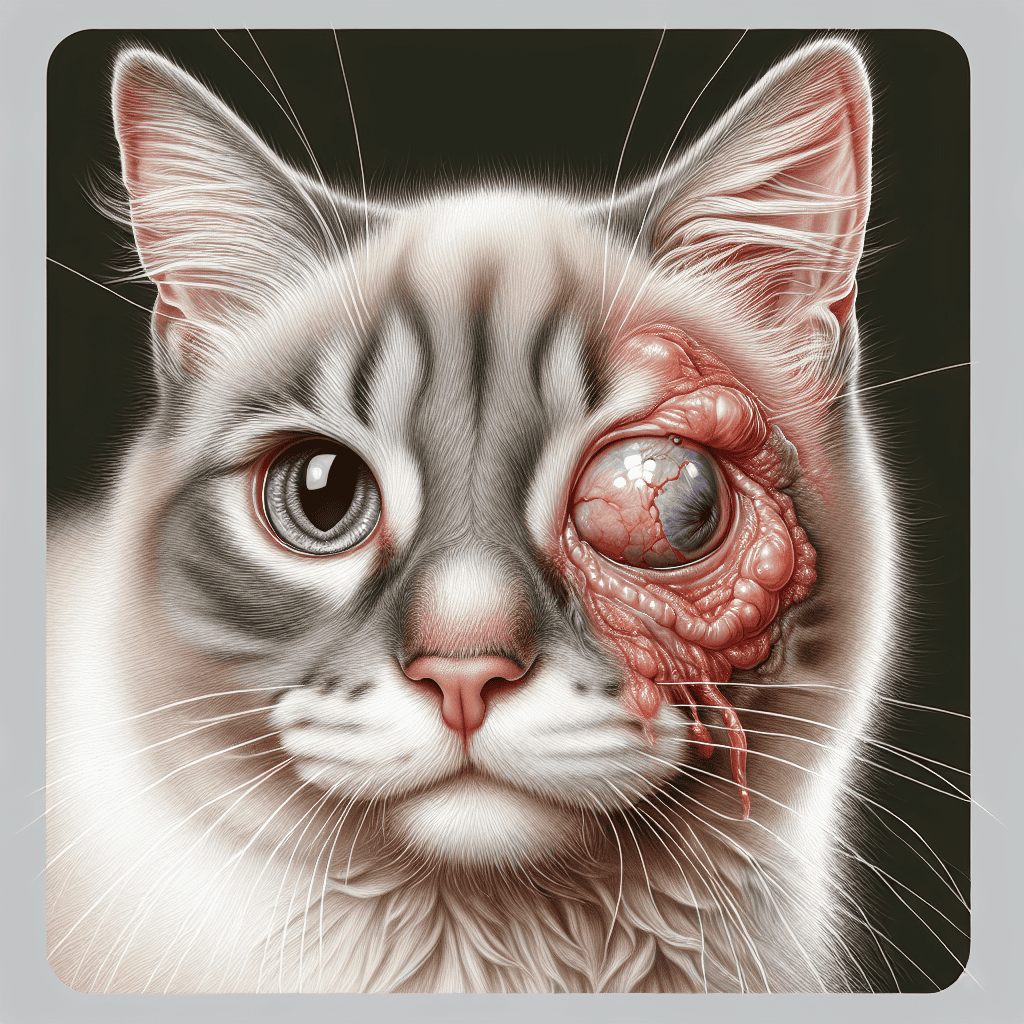
Corneal inflammation refers to the inflammation of the cornea, which is the clear outermost layer of the eye. It is characterized by the presence of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the corneal tissue. Corneal inflammation can cause various symptoms and discomfort for cats, affecting their overall eye health.
The exact cause of corneal inflammation in cats is not fully understood. However, it is believed to have both genetic and environmental factors contributing to its development. Certain breeds, such as Persians and Himalayans, are more prone to developing this condition. Environmental factors, such as allergies or infections, may trigger or exacerbate corneal inflammation.
Causes of Corneal Inflammation
The causes of corneal inflammation in cats can vary. It can be associated with underlying conditions like feline herpesvirus, which can lead to recurring episodes of inflammation. Allergies, particularly to environmental allergens or certain foods, can also contribute to corneal inflammation in cats. Other possible causes include trauma to the eye, foreign bodies, and autoimmune diseases.
Prompt veterinary diagnosis is essential to determine the underlying cause of corneal inflammation in cats. The veterinarian will perform a thorough examination, including a detailed history, physical examination, and potentially additional tests, such as corneal scraping or culture.
By understanding the overview and causes of corneal inflammation in cats, cat owners can be better prepared to recognize the signs and seek appropriate veterinary care. In the following sections, we will explore the symptoms of corneal inflammation, diagnosis, treatment options, preventive measures, and related eye conditions in cats.
Symptoms of Corneal Inflammation in Cats
Corneal inflammation, also known as eosinophilic keratitis, is a common eye condition that can affect cats. Recognizing the signs of corneal inflammation is crucial for timely intervention and appropriate treatment. Here, we will explore the key symptoms of corneal inflammation in cats and the potential impact it can have on their overall eye health.
Recognizing Corneal Inflammation Signs
When a cat experiences corneal inflammation, several noticeable signs may indicate the presence of this condition. It’s important for cat owners to be vigilant and observant of any changes in their cat’s eyes. The following signs may suggest the presence of corneal inflammation:
-
Redness and Irritation: The affected eye may appear red and inflamed. The conjunctiva, the thin tissue that covers the white part of the eye, may also become swollen and irritated.
-
Eye Discharge: Cats with corneal inflammation may exhibit excessive tearing or have a discharge from the affected eye. The discharge may vary in consistency, ranging from watery to thick and mucoid. For more information on cat eye discharge, visit our article on cat eye discharge.
-
Squinting or Blinking: Cats experiencing corneal inflammation may squint or blink frequently. This behavior is an attempt to alleviate discomfort and protect the affected eye.
-
Cloudiness or Opacity: The cornea, the transparent outer layer of the eye, may appear cloudy or hazy. This cloudiness is a result of the inflammation and can impact the cat’s vision.
-
Ulceration or Lesions: In severe cases, corneal inflammation can lead to the formation of ulcers or lesions on the surface of the eye. These sores may cause additional pain and discomfort for the cat.
If you notice any of these signs in your cat, it is crucial to seek veterinary attention promptly. A veterinarian will be able to provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Impact of Corneal Inflammation on Cats
Corneal inflammation can significantly impact a cat’s eye health and overall well-being. The inflammation can cause discomfort, pain, and vision impairment, affecting the cat’s quality of life. If left untreated, corneal inflammation can lead to complications such as corneal ulcers, infections, or scarring of the cornea.
It is important to note that corneal inflammation can have various underlying causes, including scratches, foreign objects, infections, or other systemic conditions. Therefore, identifying and addressing the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and management of the condition.
If you suspect your cat may be experiencing corneal inflammation, it is essential to consult a veterinarian. A thorough examination and appropriate diagnostic tests will help determine the underlying cause of the inflammation and guide the treatment approach.
By recognizing the symptoms of corneal inflammation and seeking timely veterinary care, you can help ensure the well-being and long-term eye health of your furry companion.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
When it comes to diagnosing and treating corneal inflammation in cats, it is essential to consult a veterinarian for a proper evaluation and guidance. Veterinary diagnosis and treatment approaches play a crucial role in managing this condition effectively.
Veterinary Diagnosis for Corneal Inflammation
To diagnose corneal inflammation (cat eye inflammation), a veterinarian will conduct a comprehensive examination of your cat’s eyes. This evaluation may include:
- Physical Examination: The veterinarian will examine the cat’s eyes, looking for any visible signs of inflammation, redness, discharge, or abnormalities.
- Fluorescein Staining: Fluorescein dye is applied to the eye’s surface to detect any corneal erosions or ulcers. The dye will highlight any irregularities on the cornea, aiding in the diagnosis.
- Schirmer Tear Test: This test measures tear production to assess if inadequate tear production is contributing to the corneal inflammation.
- Bacterial or Viral Testing: In cases where infection is suspected, the veterinarian may recommend diagnostic tests, such as bacterial or viral cultures, to identify the specific cause of the inflammation (Animal Eye Guys).
Based on the findings from these diagnostic procedures, the veterinarian will determine the underlying cause of the corneal inflammation and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Approaches for Corneal Inflammation
The treatment of corneal inflammation in cats depends on the severity, underlying cause (eosinophilic keratitis in cats), and individual cat’s needs. Some common treatment approaches include:
- Topical Medications: Veterinarians often prescribe antibiotic or antiviral eye drops or ointments to manage bacterial or viral infections associated with corneal inflammation. These medications help eliminate the infection and reduce inflammation.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: In cases of severe or chronic inflammation, corticosteroid eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Pain Management: If the cat is experiencing discomfort or pain, the veterinarian may recommend pain medications to provide relief.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: In situations where corneal inflammation is secondary to an underlying health issue, such as feline herpesvirus or allergies, treating the underlying condition is crucial for managing the corneal inflammation effectively.
- Protective Measures: To prevent further irritation and injury to the affected eye, the veterinarian may suggest using an Elizabethan collar (cone) to prevent the cat from scratching or rubbing the eye.
It is important to follow the veterinarian’s instructions regarding the proper administration of medications and any additional care needed to ensure the best possible outcome for your cat’s eye health.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are key to managing corneal inflammation in cats. If you notice any signs of eye problems in your cat, such as redness, discharge, or changes in behavior, seek veterinary attention as soon as possible to address the issue and prevent potential complications.
Preventive Measures for Corneal Inflammation
Taking preventive measures is crucial in managing and minimizing the risk of corneal inflammation in cats. By following a few simple tips and maintaining proper eye health, cat owners can help protect their feline companions from this condition. Here are some preventive measures and steps to maintain eye health in cats.
Tips to Prevent Corneal Inflammation
-
Avoid Eye Trauma: Protecting your cat’s eyes from injury is essential. Avoid situations that could lead to accidental scratching of the eye or foreign objects entering the eye. Keep a close eye on your cat during playtime and outdoor adventures to minimize the risk of eye trauma.
-
Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your veterinarian to ensure your cat’s eyes are healthy. Routine examinations can help detect any early signs of eye problems, allowing for timely intervention and treatment if necessary.
-
Monitor Eye Discharge: Keep an eye out for any unusual or excessive cat eye discharge. If you notice persistent discharge, redness, or any changes in your cat’s eye appearance, consult your veterinarian for an evaluation.
-
Maintain Cleanliness: Keep your cat’s living environment clean to reduce the likelihood of eye infections. Regularly clean their bedding, litter boxes, and any areas where they spend time to minimize the presence of irritants and potential sources of infection.
-
Avoid Irritants: Be cautious when using cleaning products, sprays, or other substances around your cat. Some chemicals can irritate their eyes and lead to inflammation. Ensure proper ventilation and keep your cat away from areas where irritants are present.
Maintaining Eye Health in Cats
In addition to preventive measures, maintaining overall eye health in cats is essential. Here are some tips to help keep your cat’s eyes healthy:
-
Proper Nutrition: Feed your cat a well-balanced diet that includes essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals. Proper nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining eye health.
-
Regular Grooming: Gently clean your cat’s face and around their eyes using a soft, damp cloth. This helps remove any debris or discharge that may accumulate, reducing the risk of eye infections.
-
Avoid Smoking: Just as secondhand smoke is harmful to humans, it can also be detrimental to animals. Avoid smoking around your cat as it can contribute to eye irritation and other health problems.
-
Provide Environmental Enrichment: Engage your cat in stimulating activities and playtime to keep them mentally and physically active. This can contribute to overall well-being, including eye health.
By following these preventive measures and maintaining good eye hygiene, cat owners can help reduce the chances of corneal inflammation and other eye-related issues. However, if you notice any signs of eye problems or suspect your cat may have developed eosinophilic keratitis or other eye conditions, it’s crucial to seek veterinary care promptly. Early intervention and appropriate treatment are key to ensuring your cat’s eye health and overall well-being.
Related Eye Conditions in Cats
In addition to corneal inflammation or eosinophilic keratitis, there are other eye conditions that can affect cats. Two common eye conditions in cats are corneal ulcers and uveitis. Let’s explore these conditions and their management.
Corneal Ulcers and Their Management
Corneal ulcers are painful sores that develop on the cornea of a cat’s eye. They can be caused by scratches, foreign objects, infections, or underlying health issues (My Vet Animal Hospital). Cats with corneal ulcers may exhibit symptoms such as squinting, discomfort in bright light, redness or inflammation in the eye, and eye drainage (PetMD).
Prompt examination and treatment are crucial for corneal ulcers, as they can quickly worsen if infected. The veterinary diagnosis for corneal ulcers involves a thorough examination of the eye using specialized equipment. Treatment approaches may include:
- Medications: Antibiotic or antifungal eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to prevent or treat infection.
- Pain relief: Pain management medications may be administered to alleviate discomfort.
- Protective measures: An Elizabethan collar (a cone-shaped collar) may be recommended to prevent the cat from scratching or rubbing the affected eye.
- Supportive care: In some cases, additional therapies such as artificial tears or topical medications to promote healing may be prescribed.
It’s important to follow the veterinarian’s instructions carefully and administer any prescribed medications as directed. Regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor the progress of the ulcer and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
Uveitis: Causes and Treatment
Uveitis is another eye condition that can affect cats. It refers to inflammation of the uvea, which includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis can be caused by various factors, including infections, underlying health issues, or trauma (Carolina Veterinary Specialists). Cats with uveitis may display symptoms such as redness, squinting, excessive tearing, eye discharge, and sensitivity to light.
The treatment for uveitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Veterinary diagnosis is crucial to identify the cause and determine the appropriate treatment. Treatment approaches for uveitis in cats may include:
- Medications: Depending on the cause, medications such as antibiotics, antiviral drugs, anti-inflammatory medications, or immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed.
- Pain relief: Pain management medications may be administered to alleviate discomfort.
- Supportive care: Additional therapies, such as lubricating eye drops or ointments, may be recommended to provide relief and support the healing process.
It’s important to follow the veterinarian’s guidance regarding the treatment plan, including the administration of medications and any necessary follow-up appointments. Regular monitoring of the cat’s eye health is essential to ensure proper management of uveitis.
By understanding these related eye conditions in cats, such as corneal ulcers and uveitis, cat owners can be vigilant in recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate veterinary care. Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the well-being and visual health of our feline companions.
Breed-Specific Eye Health Concerns
While cat eye problems can affect any feline, certain breeds are more prone to eye issues than others. Understanding these breed-specific eye health concerns can help cat owners be vigilant in monitoring their furry companions’ eye health and seek appropriate care when needed.
Breeds Prone to Eye Problems
Several breeds have a higher predisposition to eye problems. Some of the breeds known to be more susceptible to eye issues include:
| Breed | Eye Problems |
|---|---|
| Brachycephalic (squish-faced) breeds | Eye discharge, entropion (inward rolling of the eyelid), corneal ulcers |
| Persian, Exotic Shorthair, British Shorthair | Entropion, corneal sequestration (piece of cornea dies off and is pushed out of the eye) |
| Maine Coon | Entropion, corneal sequestration |
| Burmese | Prolapse of the third eyelid |
These breeds may require extra attention and regular check-ups with a veterinarian to monitor their eye health. It is important to note that while these breeds may be more prone to eye problems, it does not mean that all individuals of these breeds will develop eye issues.
Genetic Factors in Cat Eye Health
Genetics play a significant role in determining a cat’s susceptibility to eye problems. Inherited traits can contribute to various eye conditions in cats. For example, certain breeds may have a genetic predisposition to conditions like conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, glaucoma, cataracts, entropion, ectropion, third eyelid prolapse, retinal detachment, uveitis, eye infections, eye tumors, and watery eyes (The Wildest).
If you own a breed that is prone to eye problems, it is essential to be proactive in monitoring your cat’s eye health. Regular veterinary check-ups and eye examinations are crucial for early detection and treatment of any potential issues. Always consult with a veterinarian if you notice any changes in your cat’s eyes or if you have concerns about their eye health.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are key to ensuring the best possible outcome for your cat’s eye health. By staying informed about breed-specific eye health concerns and taking appropriate preventive measures, you can help safeguard your feline friend’s vision and overall well-being.