Understanding Urinary Tract Issues
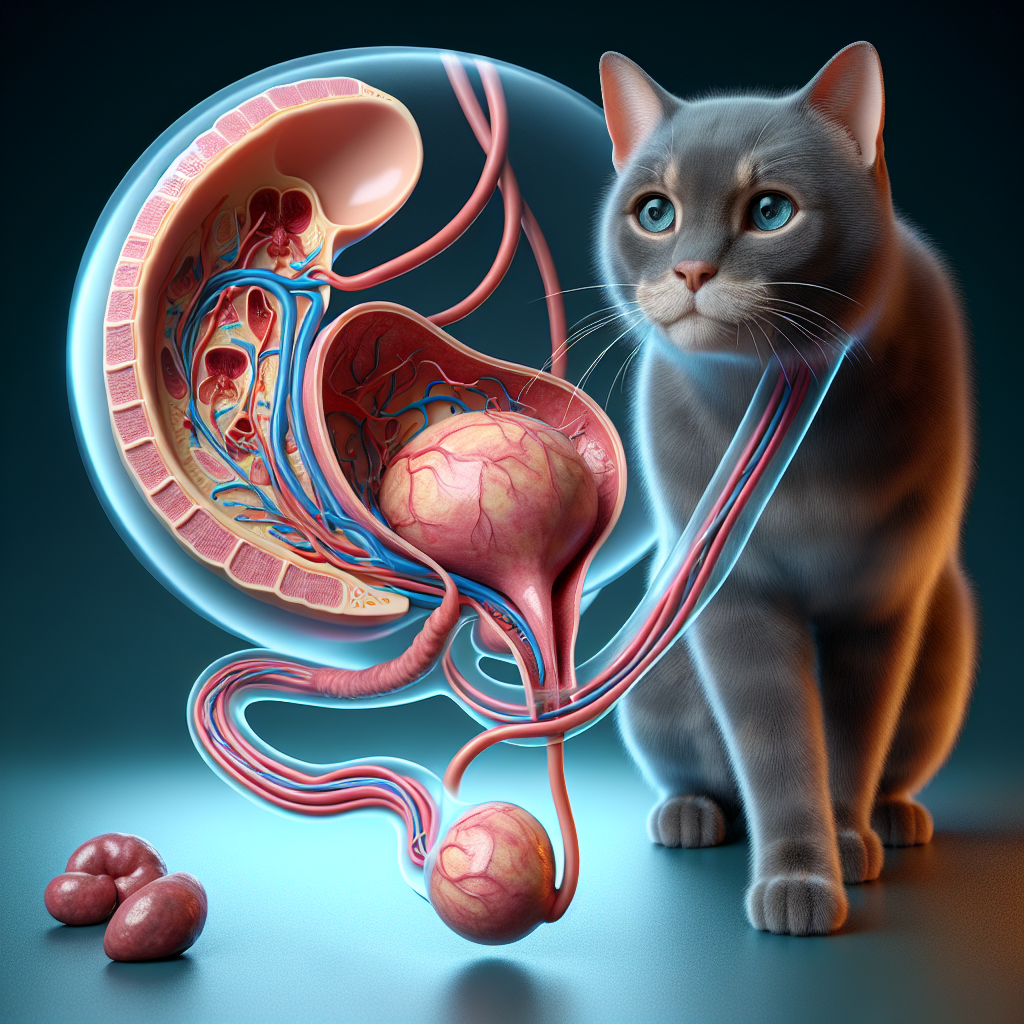
When it comes to feline health, understanding urinary tract issues is essential for maintaining your cat’s well-being. Lower urinary tract problems can affect cats of any age, and they can range from urinary tract infections (UTIs) that are resolved with antibiotics to more serious conditions like blockages and bladder stones that may require surgical intervention WebMD.
Common Symptoms in Cats
Recognizing the symptoms of urinary tract problems in cats is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Some common signs to watch for include:
- Difficulty urinating or straining to urinate
- Blood in the urine
- Urinating outside the litter box
- Excessive licking of the genital area
- Crying out while urinating WebMD.
If you notice any of these symptoms in your cat, it is important to consult a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Lower Urinary Tract Problems
There are several causes of lower urinary tract problems in cats. Some of the common culprits include:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections can occur in the urinary tract, leading to inflammation and discomfort.
- Urinary stones (uroliths): These are crystal-like formations that can form in the bladder or urethra, causing irritation and potential blockages.
- Urethral obstructions: Male cats are more prone to urethral obstructions due to their longer, narrower urethras. Blockages can be caused by urinary stones, mucus plugs, or other factors.
- Feline idiopathic cystitis (FIC): This is a condition characterized by inflammation of the bladder without a known cause. Stress and other factors may contribute to FIC.
- Diabetes: Cats with diabetes may be at an increased risk of developing urinary tract problems.
- Thyroid issues: Thyroid imbalances can affect urinary health in cats.
- Tumors: While rare, tumors in the urinary tract can lead to lower urinary tract issues WebMD.
Understanding the underlying causes of urinary tract problems in cats can help guide treatment and preventive measures. Regular veterinary check-ups and a proactive approach to feline healthcare are crucial for maintaining optimal urinary tract health.
In the following sections, we will explore specific aspects of urinary tract health, including preventive measures, management of feline lower urinary tract disease (FLUTD), and dietary considerations for urinary health.
Male Cats and Urinary Tract Health
When it comes to cat urinary tract health, male cats require special attention. Due to their longer and narrower urethras compared to female cats, they are more prone to urethral obstructions, which can be a serious and life-threatening condition (WebMD). Understanding the risk factors for urethral obstructions and the available treatments is essential for maintaining the urinary tract health of male cats.
Risk Factors for Urethral Obstructions
Several factors contribute to the increased risk of urethral obstructions in male cats. These include:
-
Anatomy: The longer and narrower urethra in male cats makes them more susceptible to blockages compared to female cats.
-
Urinary Crystals: The formation of urinary crystals can lead to the development of urethral plugs, which can obstruct the flow of urine.
-
Diet: Certain diets, particularly those high in magnesium, phosphorus, or alkaline-promoting ingredients, can increase the likelihood of crystal formation and urethral obstructions. Urinary acidifiers can be used to help maintain a healthy urinary pH.
-
Lack of Water Consumption: Inadequate water intake can contribute to concentrated urine, which may increase the risk of crystal formation and blockages.
It’s crucial to monitor male cats closely for any signs of urinary problems and take appropriate preventive measures to minimize the risk of urethral obstructions.
Treatment for Urethral Blockages
Urethral blockages are considered medical emergencies, and immediate veterinary attention is necessary. The treatment for urethral blockages in male cats may include:
-
Catheterization: A urinary catheter is inserted to relieve the obstruction and allow the flow of urine. This procedure is typically performed under anesthesia.
-
Fluid Therapy: Intravenous fluids may be administered to correct dehydration and restore electrolyte balance.
-
Medication: Pain relief medication and medications to relax the urethral muscles may be prescribed to facilitate the passage of the obstruction.
In severe cases or when the obstruction cannot be relieved through catheterization, surgery may be necessary to remove the blockage.
Preventive measures, such as dietary modifications to promote urinary health, increased water intake, and regular veterinary check-ups, play a crucial role in reducing the risk of urethral obstructions in male cats. By being proactive in managing their urinary tract health, cat owners can help ensure the well-being of their feline companions.
Preventive Measures for Urinary Health
Taking preventive measures is crucial for maintaining the urinary health of your cat. By focusing on two key aspects – water intake and diet – you can help promote a healthy urinary tract and prevent potential issues.
Importance of Water Intake
Water intake plays a vital role in maintaining a cat’s urinary health. Sufficient water consumption helps dilute minerals in the urine, preventing the formation of crystals and bladder stones. Cats are naturally thirst-tolerant animals, and it’s essential to provide them with access to fresh water at all times. Consider using a “kitty fountain” or multiple water bowls to encourage water intake (The Spruce Pets).
To ensure your cat is well-hydrated, monitor their water intake and take note of any changes in consumption. If you notice a decrease in water intake or suspect dehydration, consult with your veterinarian for guidance.
Impact of Diet on Urinary Health
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining urinary health in cats. Good quality canned cat foods are generally better for urinary health than dry foods. The additional moisture content in canned food helps increase overall water intake, ensuring proper hydration and dilution of minerals in the urine. Even if you choose a high-quality dry food, it’s essential to supplement your cat’s diet with canned food or by soaking the kibble in water before serving.
Scientific research and feeding trials have shown that the Relative Super Saturation (RSS) factor and urine pH are crucial in preventing the formation of urine crystals in a cat’s bladder. It’s important to feed diets formulated to control these properties to prevent the formation of crystals and potential urinary tract issues (Killarney Cat Hospital).
When selecting cat food, look for options specifically formulated for urinary health. These diets are designed to promote a proper urine pH balance and minimize the risk of crystal formation. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the most suitable diet for your cat’s specific needs.
By prioritizing water intake and choosing a diet that supports urinary health, you can take proactive steps to prevent urinary problems in your cat. Regular veterinary check-ups are also essential to monitor your cat’s overall health and identify any potential issues early on. Remember, preventive measures are key to ensuring your cat’s well-being and avoiding potential urinary tract emergencies.
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD)
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) is an umbrella term that encompasses various clinical symptoms and conditions affecting the urinary system of cats. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of FLUTD and understand the management and treatment approaches.
Signs and Symptoms of FLUTD
Cats suffering from FLUTD may exhibit a range of signs and symptoms, which can vary in severity. Some common signs of FLUTD include:
- Difficulty urinating: Cats may experience pain or discomfort while urinating and may strain or show signs of distress.
- Blood in urine: Hematuria, the presence of blood in the urine, is a common indicator of FLUTD.
- Excessive licking of the genital area: Cats with FLUTD may excessively groom their genital area as a response to discomfort.
- Urinating outside the litter box: Cats may urinate outside of their litter box, often on cool surfaces like bathtubs or tile floors.
- Urinary blockage: In some cases, FLUTD can lead to a complete obstruction of the urethra, which can be life-threatening. Cats with an obstructed urethra may pass little or no urine and exhibit increasing distress.
It is important to note that the signs and symptoms of FLUTD can also overlap with other urinary problems in cats. Therefore, a proper diagnosis from a veterinarian is crucial for accurate treatment.
Management and Treatment Approaches
The management and treatment of FLUTD depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common approaches include:
- Medical management: In cases of FLUTD caused by urinary crystals or stones, medical management may involve dietary changes to address the pH balance of the urine. For instance, urinary acidifiers may be prescribed to decrease the alkaline urine pH associated with crystal formation. However, it is essential to consult with a veterinarian before making any dietary changes.
- Environmental modifications: Stress or anxiety can contribute to Feline Idiopathic Cystitis (FIC), a common cause of FLUTD. Creating a calm and stress-free environment for cats can help manage FIC.
- Medications: In certain cases, medications may be prescribed to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, or manage underlying medical conditions that contribute to FLUTD.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases of urinary blockage, where the urethra is completely obstructed, emergency surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve the obstruction and restore normal urinary flow.
Proper veterinary care and regular check-ups are crucial for managing FLUTD. It is essential to closely follow the advice and recommendations of a veterinarian to ensure the well-being and urinary tract health of your cat. For more information on preventive healthcare for cats, including the importance of regular check-ups and dental care, refer to our article on preventive healthcare for cats.
Understanding the signs, symptoms, and treatment approaches for FLUTD empowers cat owners to recognize potential issues and seek appropriate veterinary care promptly. By addressing feline lower urinary tract disease early on, we can help ensure the well-being and urinary health of our feline companions.
Preventive Healthcare for Cats
Taking proactive measures to ensure the health and well-being of your cat is essential. Regular check-ups and preventive care play a crucial role in maintaining a cat’s overall health. In this section, we will discuss the importance of regular check-ups and dental care as part of preventive healthcare for cats.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are an integral part of preventive healthcare for cats. These check-ups provide an opportunity for your veterinarian to assess your cat’s overall health, detect any early signs of illness, and recommend appropriate interventions. Annual check-ups are typically recommended, but more frequent visits may be necessary for older cats or those with specific health concerns.
During a check-up, your veterinarian may perform a variety of tests and screenings, such as blood tests and urinalysis, to evaluate your cat’s organ function and detect any underlying issues. These screenings can help identify potential health problems before they become more serious (VCA Hospitals). Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity for you to discuss any concerns or observations you may have about your cat’s behavior or well-being.
Dental Care and Preventive Measures
Dental care is another crucial aspect of preventive healthcare for cats. Poor oral health can have a significant impact on a cat’s overall well-being. Dental disease, such as periodontal disease, can lead to the spread of bacteria to major organs, causing serious health problems.
To maintain good dental health, cats may require regular dental cleanings. The frequency of cleanings can vary depending on the individual cat’s oral health, but generally, cats may need their teeth cleaned every one to two years. Dental radiographs may also be performed during these cleanings to assess the severity of oral disease.
As a cat owner, you can also take preventive measures to promote good dental health. These include regular toothbrushing using cat-friendly toothpaste, providing dental treats or toys, and incorporating dental diets into their feeding routine. Your veterinarian can provide guidance on the best dental care practices for your cat.
Remember, preventive healthcare for cats goes beyond regular check-ups and dental care. It also includes measures such as testing for heartworms, intestinal parasites, and other conditions. Blood tests, urinalysis, and screenings for diseases like FIV and feline leukemia virus are recommended at least once a year, with more frequent testing if problems are diagnosed. Additionally, cats should be given medication to prevent heartworms, intestinal parasites, fleas, and ticks, based on their health status, outdoor access, and environmental risks.
Spaying or neutering cats also plays a crucial role in preventive healthcare. These procedures offer various health and behavioral benefits, including the prevention of infections and certain types of cancer. It’s important to discuss the benefits and timing of spaying or neutering with your veterinarian to ensure the best care for your cat.
By prioritizing regular check-ups, dental care, and other preventive measures, you can help ensure the long-term health and well-being of your feline companion. Your veterinarian is a valuable resource for guidance and advice on preventive healthcare tailored to your cat’s specific needs.
Dietary Considerations for Urinary Health
When it comes to maintaining optimal urinary tract health in cats, diet plays a crucial role. By understanding the role of diet in preventing urinary crystals and implementing appropriate feeding strategies, cat owners can help promote a healthy urinary system for their feline companions.
Role of Diet in Preventing Crystals
The formation of urinary crystals is influenced by various factors, including diet. It is important to note that special diets designed to prevent the formation of one type of crystal can potentially cause the formation of another type (The Spruce Pets). Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a veterinarian before making any significant dietary changes for your cat.
The pH of urine, the dilution of urine, and non-dietary factors all play significant roles in urinary tract health. Ensuring that your cat’s urine is sufficiently diluted by providing access to plain water is crucial. Cats naturally have a low thirst drive, so strategies to increase water intake are important. This can be achieved by using a “kitty fountain” or providing fresh water in multiple bowls to encourage drinking (The Spruce Pets).
Feeding Strategies for Urinary Health
Choosing the right type of food for your cat’s urinary health is essential. Good quality canned cat foods are generally better for urinary health compared to dry foods. Even if you opt for a high-quality dry food, it is important to supplement your cat’s diet with a small amount of canned food each day or consider soaking the kibble in water before serving. These measures help increase the moisture content of the overall diet, aiding in the dilution of urine and reducing the risk of crystal formation.
It is crucial to ensure that your cat has access to fresh, clean water at all times. Water intake is particularly important for maintaining urinary tract health, as neither crystals nor bladder stones can form when minerals are sufficiently diluted. Avoid feeding table scraps, as they may contain ingredients that can be detrimental to urinary health.
By feeding diets formulated to control factors such as Relative Super Saturation (RSS) factor and urine pH, you can help prevent the formation of urine crystals and potential urinary tract issues. These diets are designed to provide the necessary balance of nutrients while promoting a healthy urinary system (Killarney Cat Hospital).
In conclusion, paying attention to your cat’s diet is crucial for maintaining urinary tract health. By considering the role of diet in preventing crystals and implementing appropriate feeding strategies, you can help promote a healthy urinary system for your feline companion. Remember to consult with a veterinarian to ensure that you are providing the most suitable diet for your cat’s specific needs.