Understanding Dog Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, are a skin condition that can affect dogs. Understanding the definition and causes of dog hives is essential for identifying and managing this condition.
Definition of Dog Hives
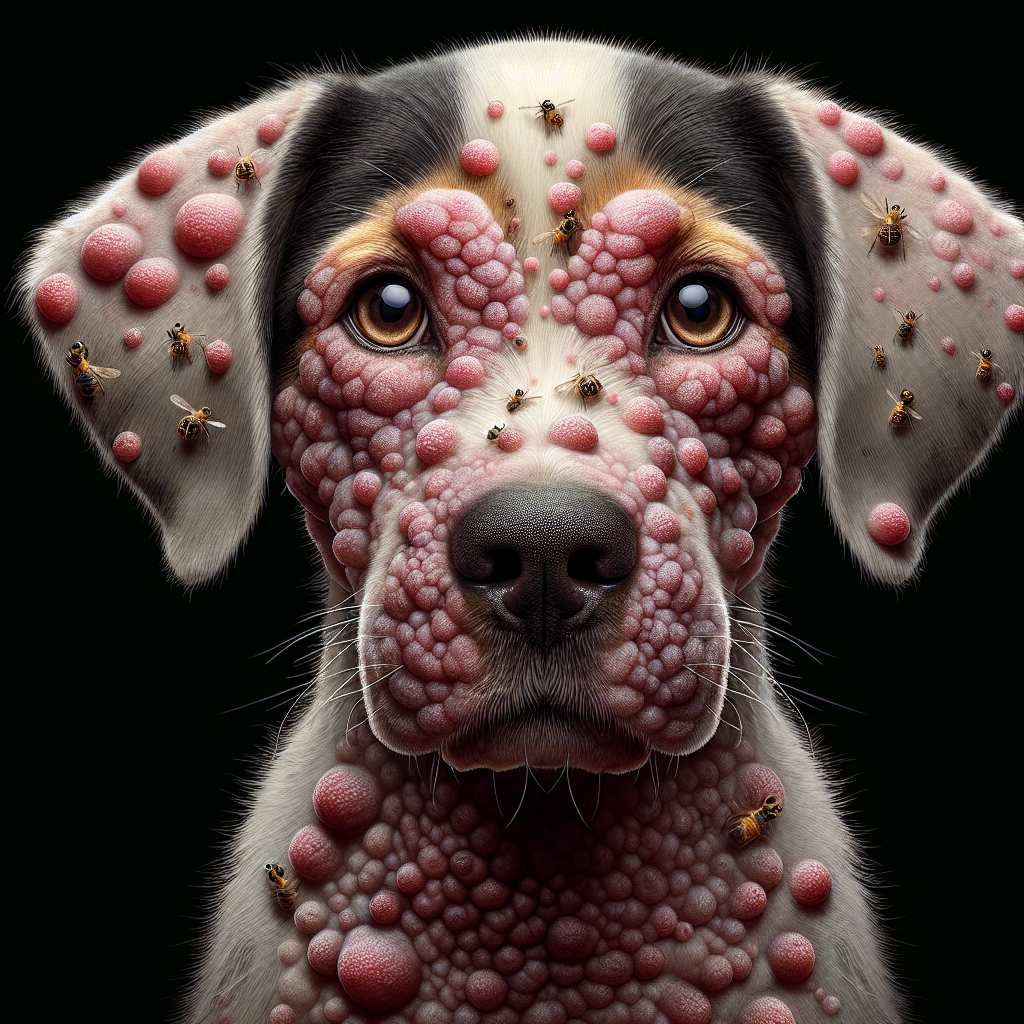
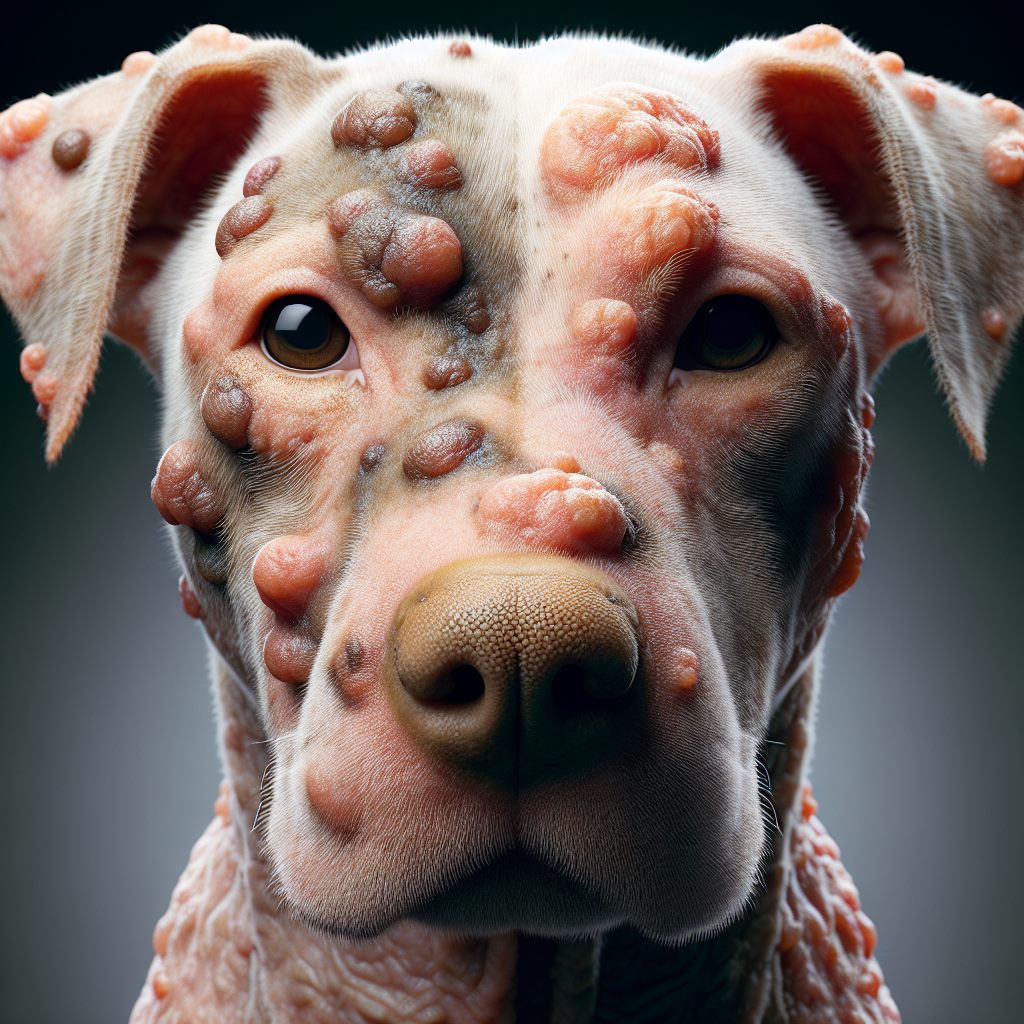
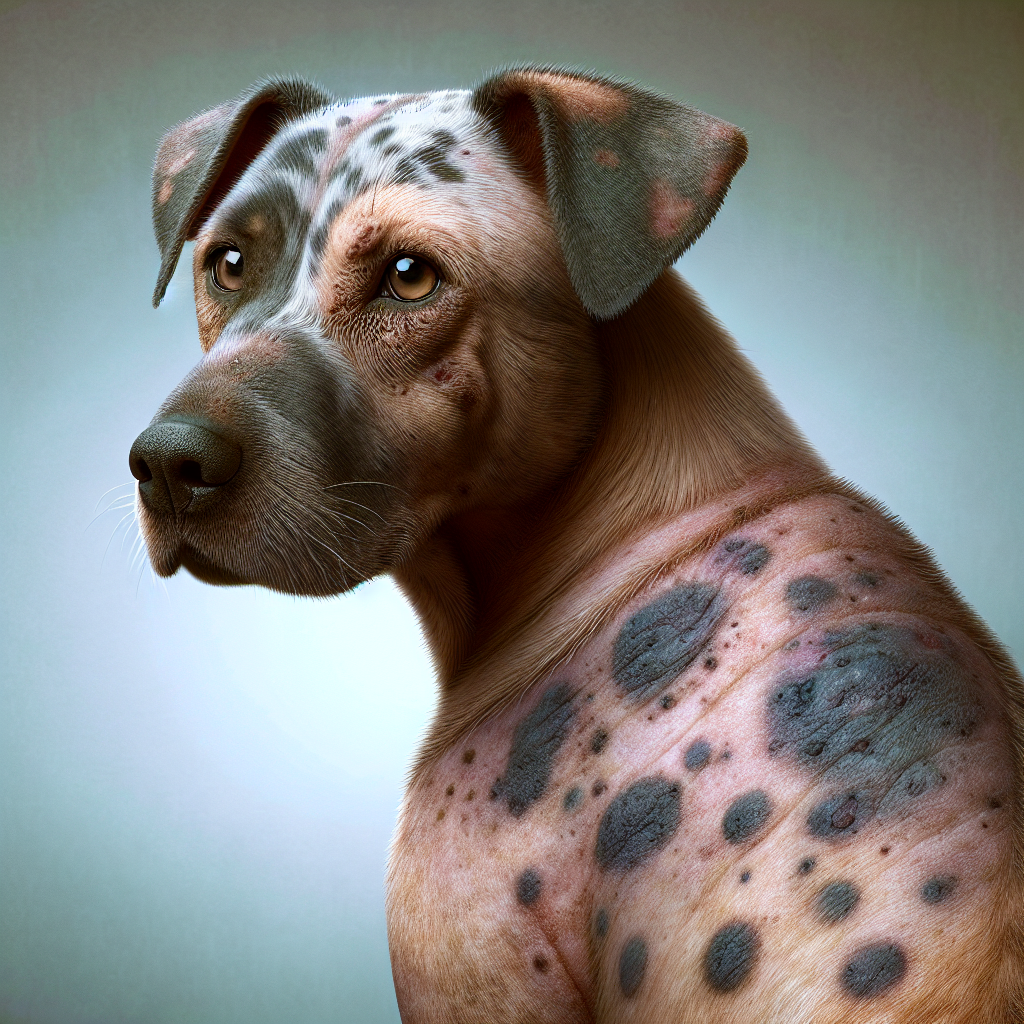
Urticaria, or hives, in dogs is characterized by raised red welts on the skin. These welts can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, lips, tongue, throat, and ears. The size of the welts can vary, ranging from about 5 mm to several cm in diameter. In some cases, if there are many welts, they can blend together. Hives are typically very itchy, causing discomfort for the dog (VCA Hospitals).
Causes of Dog Hives
Hives in dogs are almost always a symptom of an allergic reaction. Several factors can trigger an allergic reaction leading to hives in dogs. The most common causes include:
- Insect bites/stings: Insects such as fleas, mosquitoes, or bees can cause hives in dogs.
- Chemical contact: Contact with certain shampoos, soaps, or other chemicals can trigger an allergic reaction and result in hives.
- Medications: Some medications can cause hives as an adverse reaction.
- Toxic plants: Contact with certain plants, such as poison ivy or poison oak, can lead to hives.
- Food allergens: Dogs can develop hives as a result of an allergic reaction to specific foods (PetMD).
It’s important to note that hives in dogs can also be associated with anxiety in extremely anxious dogs. However, allergic reactions remain the most common cause of hives in dogs (Heart and Paw).
Identifying the underlying cause of hives in dogs is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of future episodes. If your dog experiences hives, it is recommended to seek veterinary care to determine the cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. For more information on the treatment options for dog hives, refer to our article on dog hives treatment.
In the next section, we will explore the signs of dog hives and how they can be diagnosed.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
When it comes to identifying and diagnosing dog hives, it’s essential to be aware of the signs and understand the diagnostic process. This section will cover the common signs of dog hives and the steps involved in diagnosing this condition.
Signs of Dog Hives
Dog hives, also known as urticaria, appear as raised red welts on the skin (PetMD). These wheals can vary in size and are usually very itchy. Hives can develop on any part of the body, but they are commonly found on the head, neck, back, abdomen, and legs (VCA Hospitals). In severe cases, hives may also affect mucous membranes such as the mouth, nose, eyes, rectum, and vagina (Merck Veterinary Manual).
The primary symptoms of dog hives include:
- Raised red welts on the skin
- Itching and scratching
- Swelling of the affected areas
- Excessive drooling if the mouth is swollen
- Swelling of the face and respiratory system (angioedema), which can be a cause for concern (PetMD)
If you notice these symptoms in your dog, it is important to seek veterinary care for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing Dog Hives
To diagnose dog hives, a veterinarian will perform a thorough examination of your dog’s skin and inquire about any recent changes in their environment, diet, or exposure to potential allergens. The diagnostic process may include:
-
Physical Examination: The veterinarian will visually inspect the dog’s skin to identify the presence of hives and assess the severity of the condition.
-
Medical History: The veterinarian will ask about any recent changes in the dog’s routine, diet, or exposure to potential allergens. This information can provide valuable insights into the underlying cause of the hives.
-
Allergy Testing: In some cases, allergy testing may be recommended to identify specific allergens that trigger the hives. This can help determine the appropriate treatment and prevention strategies.
-
Elimination Diet: If food allergies are suspected, the veterinarian may recommend an elimination diet to identify potential food triggers. This involves removing certain ingredients from the dog’s diet and gradually reintroducing them to identify any allergic reactions.
Diagnosing dog hives involves a combination of clinical observation, medical history, and, in some cases, specialized testing. It is crucial to consult with a veterinarian to accurately diagnose the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
In the next section, we will explore various treatment options for managing dog hives, including mild and severe allergic reactions. For more information regarding specific causes of dog hives, refer to our article on dog hives causes.
Treatment Options
When it comes to treating dog hives, the approach may vary depending on the severity of the allergic reaction. Treatment options for dog hives can be categorized into mild allergic reactions and severe allergic reactions.
Mild Allergic Reactions
For cases of mild allergic reactions in dogs, treatment typically involves administering antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and sometimes corticosteroids. Antihistamines work by blocking the histamine receptors in the body, helping to alleviate itching and reduce the allergic response. Cetirizine has also shown effectiveness in reducing dermatologic symptoms and gastrointestinal signs in dogs.
In addition to medication, providing relief from itching is essential. This can include using cold compresses over the hives or applying topical treatments recommended by a veterinarian. It’s important to consult a veterinarian for appropriate dosages and guidance on using antihistamines for your dog.
Severe Allergic Reactions
Severe, life-threatening allergic reactions may require immediate veterinary care. In these situations, treatment may involve more aggressive measures. It is crucial to seek veterinary attention promptly to ensure the best outcome for your dog.
In cases of severe allergic reactions, the veterinarian may administer injectable medications, including antihistamines and corticosteroids, to rapidly reduce the allergic response. Intravenous fluids may also be administered to maintain hydration and stabilize the dog’s condition.
In extreme cases where there is a risk of anaphylaxis or difficulty breathing, epinephrine may be required to counteract the severe allergic reaction. Epinephrine is typically administered through an injection and should only be done by a trained professional.
Hospitalization for further treatment and monitoring may be necessary for dogs experiencing severe allergic reactions. It allows for close observation and ensures that any potential complications are addressed promptly.
Remember, it is vital to consult with a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for your dog’s specific condition. They will be able to assess the severity of the allergic reaction and recommend the most suitable treatment options.
For more information on dog hives, including their causes and symptoms, refer to our earlier sections on dog hives causes and signs of dog hives.
Preventing and Managing Hives
Preventing and managing hives in dogs is essential to ensure their well-being and minimize discomfort. By implementing effective prevention strategies and addressing the underlying causes, dog owners can help reduce the occurrence of hives in their pets.
Prevention Strategies
To prevent hives in dogs, it’s important to identify and avoid potential triggers. Retracing the dog’s activities and monitoring their environment can help pinpoint potential allergens or irritants. Some common prevention strategies include:
-
Environmental Control: Minimize exposure to known allergens such as certain plants, insect bites, or chemicals. This may involve keeping dogs away from specific areas or using protective measures like insect repellents or pet-safe sunscreen.
-
Dietary Management: If food allergies are suspected, work with a veterinarian to identify and eliminate potential allergens from the dog’s diet. This may involve conducting an elimination diet or switching to hypoallergenic or limited ingredient diets.
-
Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Routine veterinary check-ups can help detect and address any underlying health issues that may contribute to hives. Regular vaccinations and parasite prevention are also important in maintaining overall health.
-
Avoiding Overheating: Dogs prone to heat-related hives should be kept in a cool and well-ventilated environment. Avoid exposing them to excessive heat and ensure they have access to fresh water at all times.
-
Monitoring Medications: Some medications can trigger allergic reactions in dogs. It’s crucial to inform the veterinarian about any medications the dog is taking and to be vigilant for signs of hives or other adverse reactions.
Recurrence of Dog Hives
Dogs that have experienced hives once are at risk of having them recur in the future. Therefore, it’s important to identify and manage the underlying cause to prevent their recurrence. This may involve retracing the dog’s activities to pinpoint potential triggers such as new plants, food, insect bites, or medications. Working closely with a veterinarian can help in determining the cause and developing an appropriate management plan.
If hives do recur despite preventive measures, it’s essential to consult a veterinarian for further evaluation. They may recommend additional diagnostic tests or adjustments to the prevention strategies. Remember, it’s crucial not to administer human allergy medications like Benadryl to dogs without veterinary guidance. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for effectively managing and preventing the recurrence of dog hives.
While hives in dogs are generally not fatal, it’s important to note that severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis or swelling of the respiratory tract, can be life-threatening. Therefore, if a dog’s hives last for several hours or more, immediate veterinary attention is necessary. Taking the dog to an emergency veterinarian or regular veterinarian for evaluation and treatment is highly recommended.
By implementing preventive measures, identifying triggers, and seeking veterinary guidance, dog owners can effectively manage and reduce the occurrence of hives in their furry companions. Stay vigilant, follow preventive strategies, and provide appropriate care to keep your dog healthy and comfortable. For information on treatment options for dog hives, refer to our article on dog hives treatment.
Emergency Situations
When it comes to dog hives, it’s important to be aware of situations that require immediate veterinary care. Hives in dogs are considered an emergency as they indicate an allergic reaction within the body, which could lead to dangerous complications like anaphylaxis and even death. It is recommended to seek veterinary treatment for hives, even in mild cases, to prevent potential complications (PetMD).
When to Seek Veterinary Care
If your dog develops hives, it’s crucial to monitor the situation closely. While mild cases of hives may resolve on their own within 12-48 hours after contact with the allergen, it’s essential to seek veterinary care whenever hives are observed, especially if they occur on the face or around the throat. The following situations warrant immediate veterinary attention:
-
Severe Facial Swelling: If your dog’s face becomes significantly swollen, especially around the eyes or muzzle, it may indicate a severe allergic reaction that requires prompt veterinary assessment.
-
Difficulty Breathing: If your dog experiences difficulty breathing, such as rapid or labored breathing, wheezing, coughing, or excessive panting, it could signify a severe allergic reaction that requires immediate veterinary intervention.
-
Excessive Drooling: Excessive drooling, particularly if the mouth or tongue appears swollen, is a concerning sign that should prompt you to seek veterinary care promptly.
-
Widespread Hives: If your dog develops hives all over their body, including on the back, flanks, neck, eyelids, and legs, it may indicate a severe allergic reaction. Veterinary attention is necessary to evaluate and manage the situation.
Remember, hives in dogs can be unpredictable, and the severity of the reaction can escalate rapidly. It’s better to err on the side of caution and seek veterinary care if you have any concerns about your dog’s condition.
Immediate Actions for Severe Hives
While waiting for veterinary care, there are a few immediate actions you can take to help your dog if they are experiencing severe hives:
-
Remove the Allergen: If you suspect that your dog has come into contact with an allergen, such as a plant or a chemical, try to remove them from the environment or wash off any residual allergen from their fur with mild pet-friendly shampoo.
-
Keep Calm: Keep your dog calm and minimize any additional stress as it can worsen the allergic reaction. Speak to them in a soothing tone and provide a quiet and comfortable environment.
-
Avoid Self-Medication: It’s crucial not to administer any medications to your dog without veterinary guidance. Some human medications can be toxic to dogs and may worsen the situation.
Remember, these immediate actions are temporary measures and should not replace veterinary care. Once your dog receives appropriate medical attention, the veterinarian will determine the best course of treatment based on the severity of the hives and the underlying cause.
By recognizing the signs that require immediate veterinary care and taking prompt action, you can ensure the health and well-being of your dog during an episode of severe hives. For more information on the treatment options for dog hives, refer to our article on dog hives treatment.